3 commonly flow problems “Rat-holing”, Mechanical arching and Cohesive arching.
Problems That Are Frequently Encountered Involve:
- Erratic flow
- Flooding
- “Rat-holing” & blockage
- Mechanical & cohesive arching
- Segregation
- Degradation
- Lack of storage capacity
Flow Mass
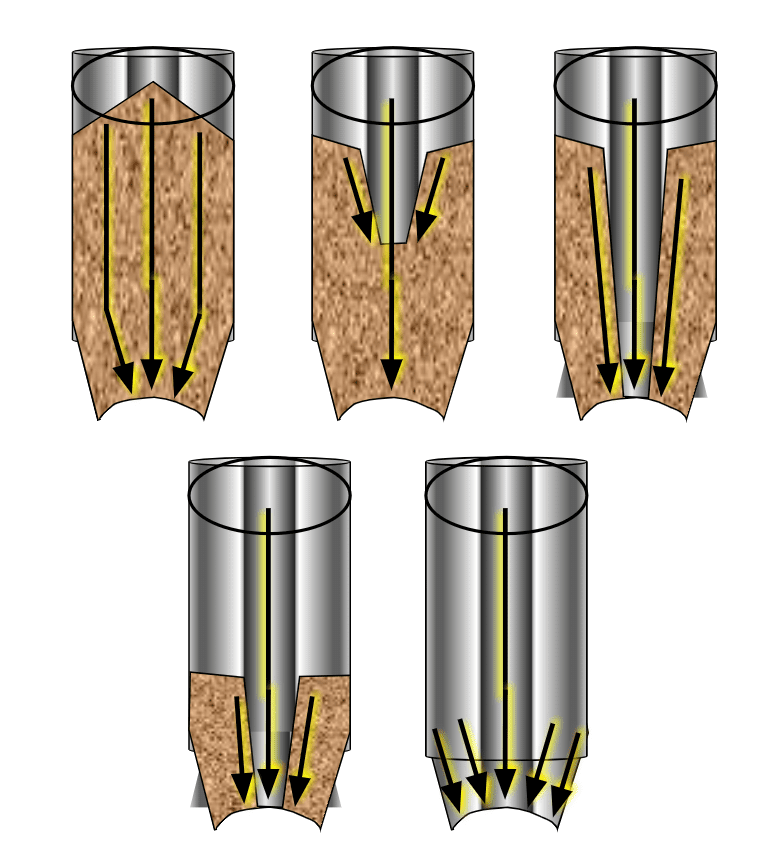
In a Mass Flow silo, the walls are steep and smooth enough to ensure flow of all particles.
Mass Flow Key Features
- “first in – first out”
- All storage capacity is “live”
- Minimize segregation
- Hopper half angle [Θ] is typically < 25° (from vertical)
- Even flow
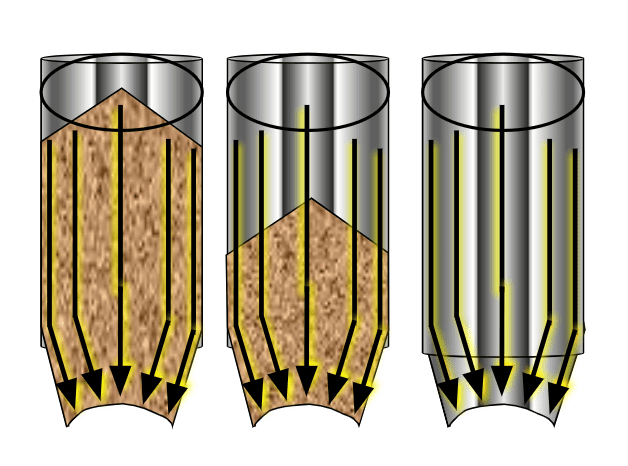
Core Flow
It occurs when the silo is not steep or smooth enough to force the bulk material to slide along the walls. It also occurs when the outlet of the silo is not large enough or fully effective.
Core Flow Key Features
- “first in – last out”
- “dead” regions of product
- Exaggerates segregation effects on particles
- Hopper half angle [Θ] is typically > 25° (from vertical)
- Erratic flow
Core Flow Can
It can result in “rat-holing” when sloughing off of material from the top does not occur, due to the cohesive strength of the material.
“Rat-Holing”
It occurs when the central core has been discharged, whilst leaving the majority of the product supporting itself around the inside of the silo.

Bulk Material Analysis
“design a mass flow bin, hopper or silo”
Objective Of Bulk Material Analysis:
- Determination of:
- 1. Standard properties of bulk material
- Density {packed & unpacked}
- Angle of repose {static & dynamic}
- Critical values of moisture
- Wall friction angle [φx ]
- Angle of inner friction [φe ]
- Angle of slide [Θ]
- Minimum silo outlet opening required for mass flow
- Considering various liner materials
- Considering time consolidation
- 1. Standard properties of bulk material
Critical Moisture

Moisture Measurement
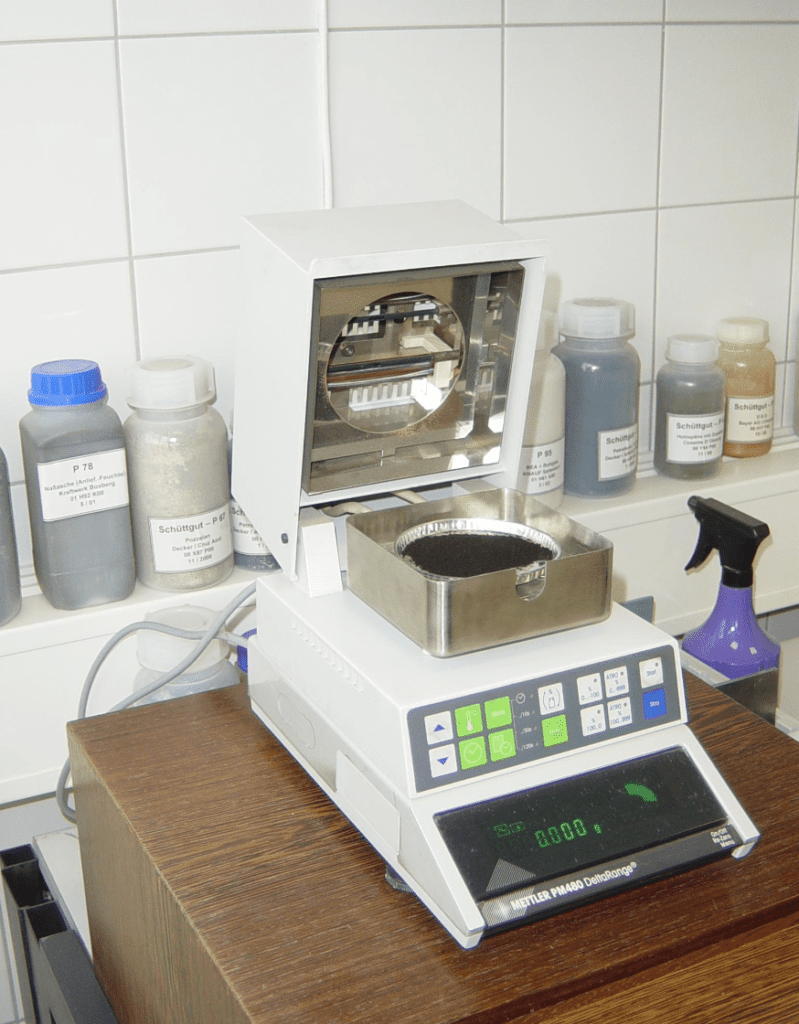

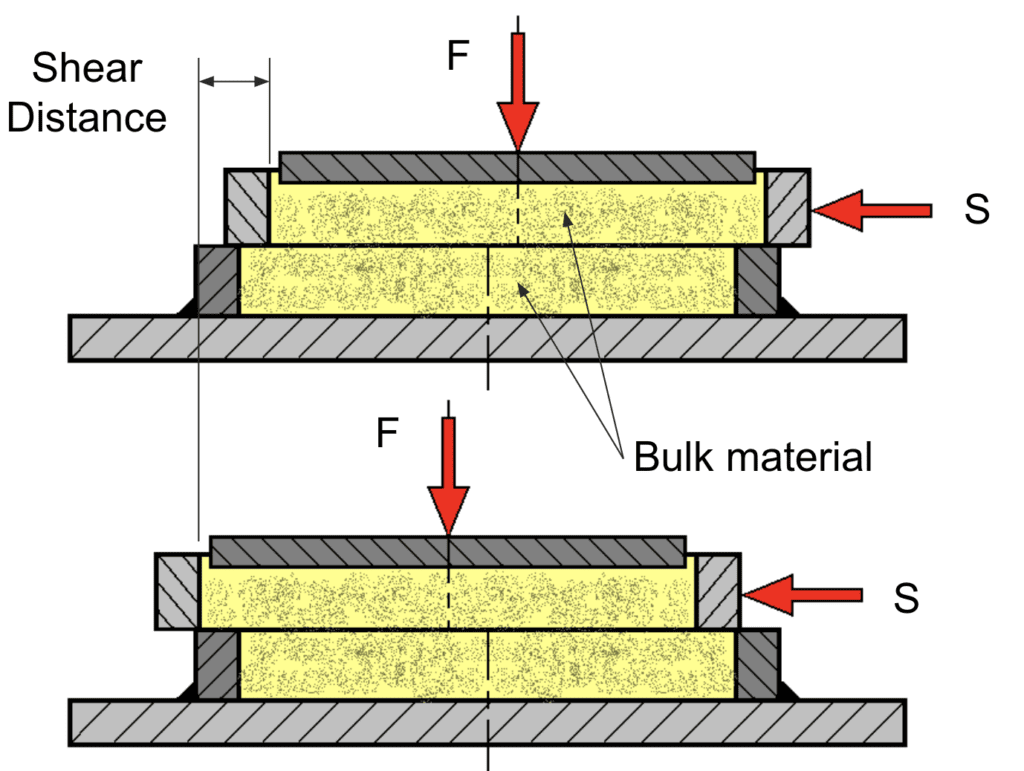
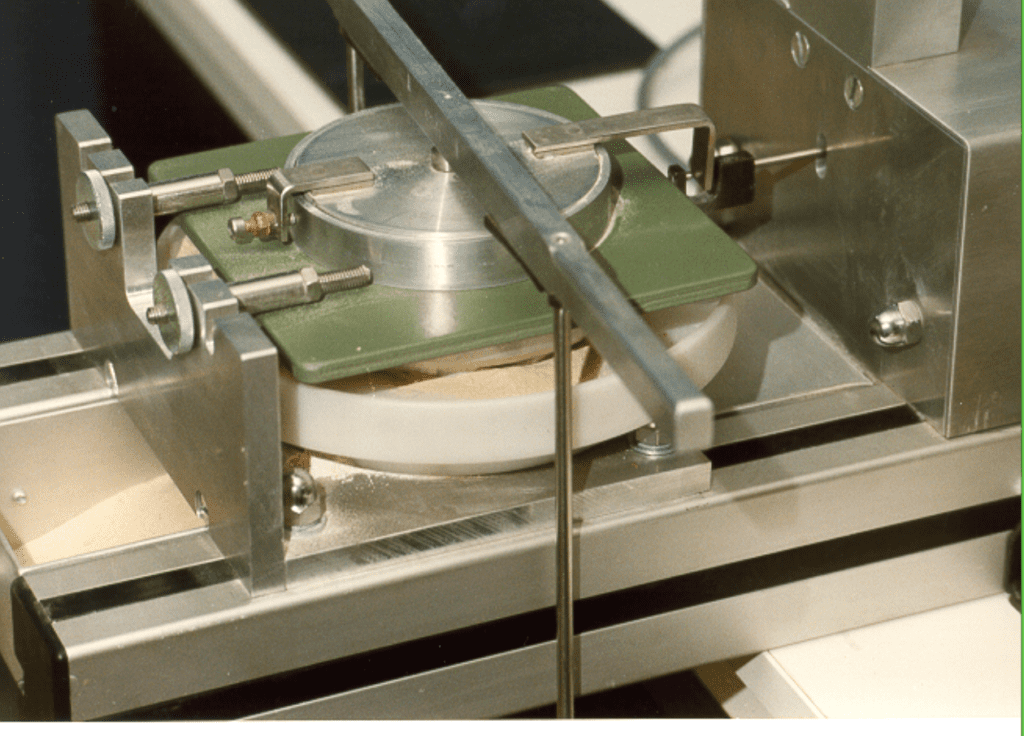
Bulk Material Testing
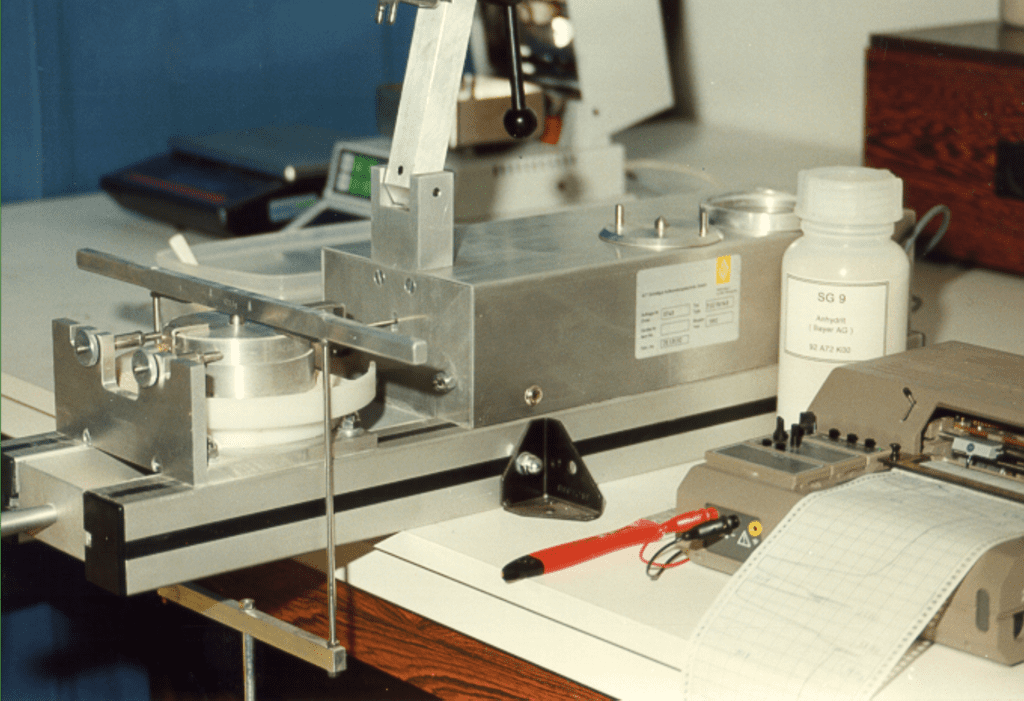
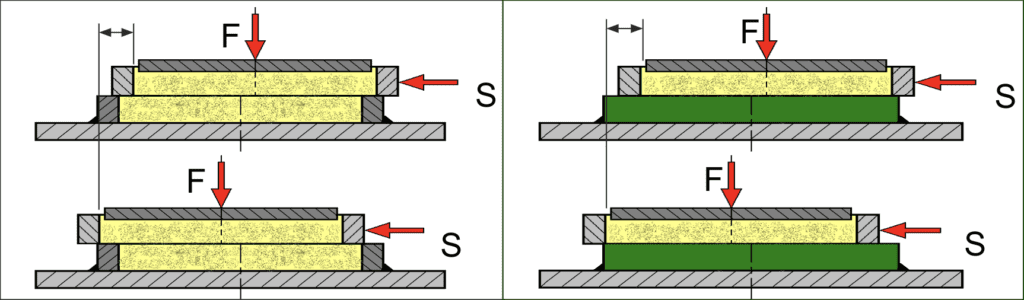
Shear Cell
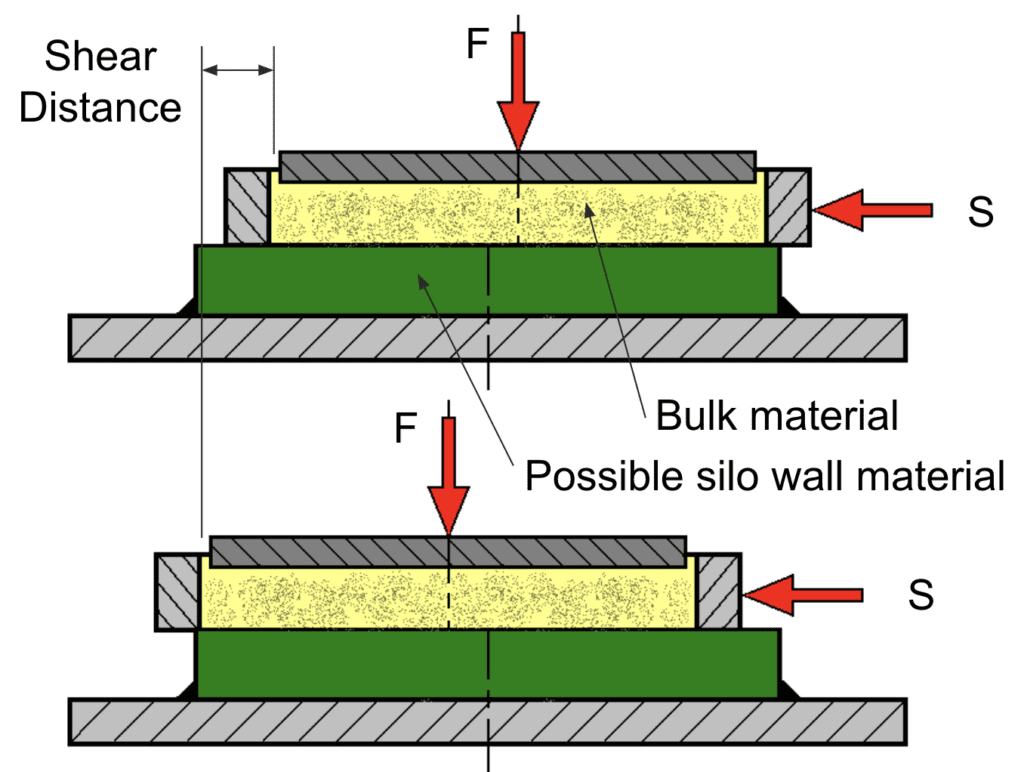
Ring Shear Cell
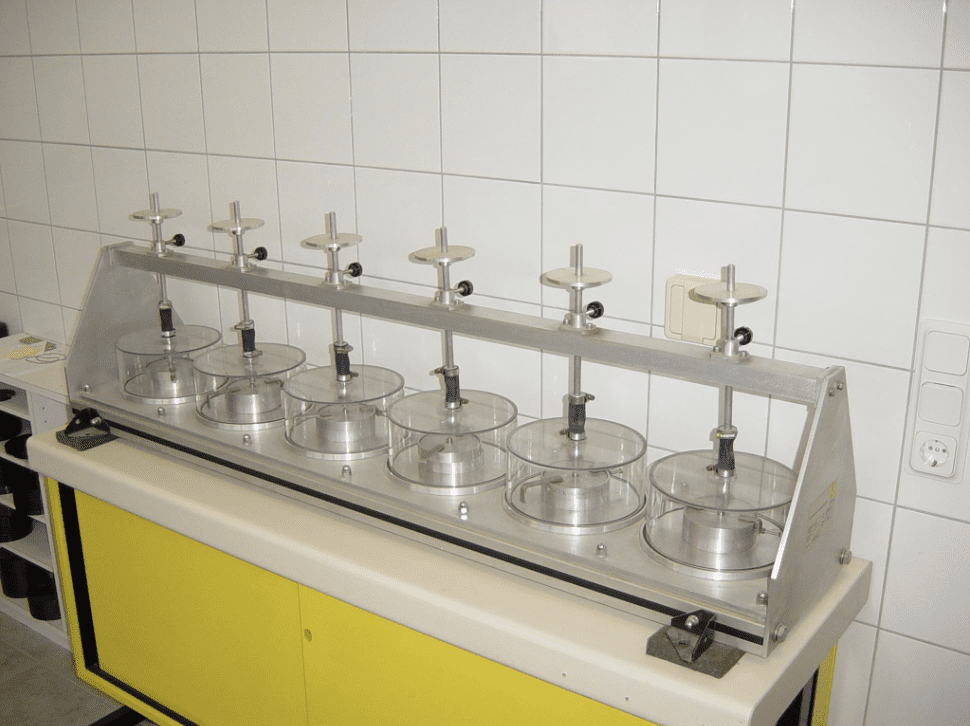
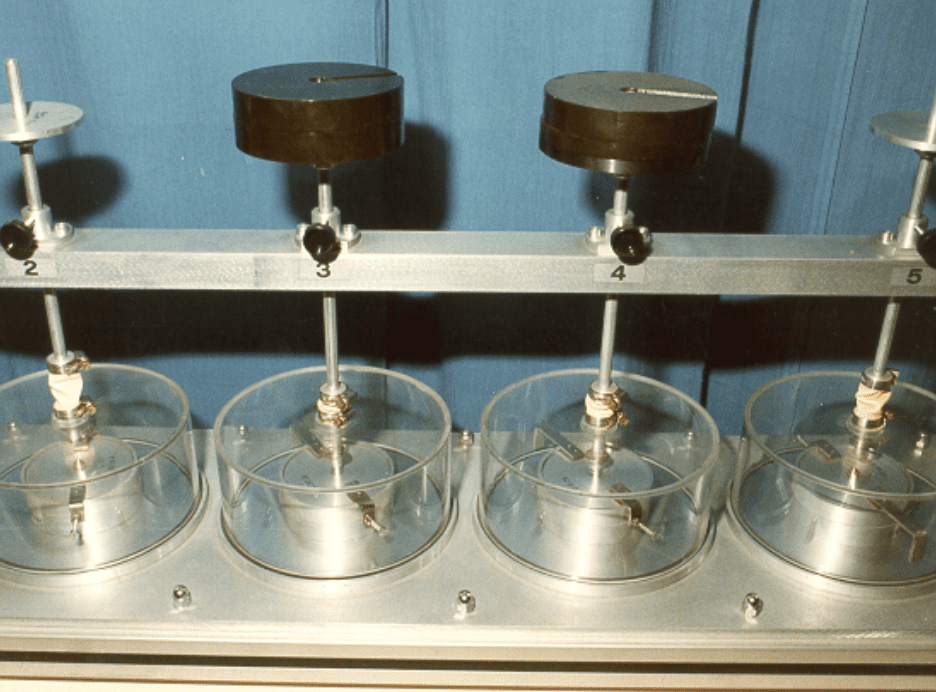
Time Consolidation
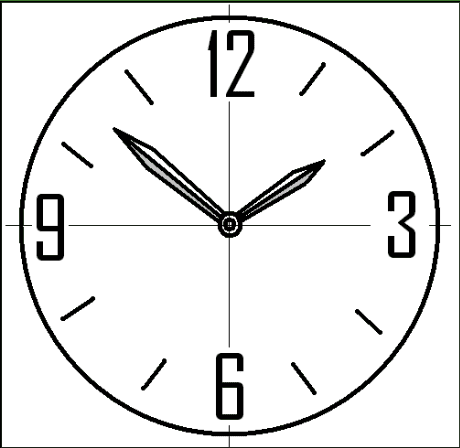
Time Consolidation Bench

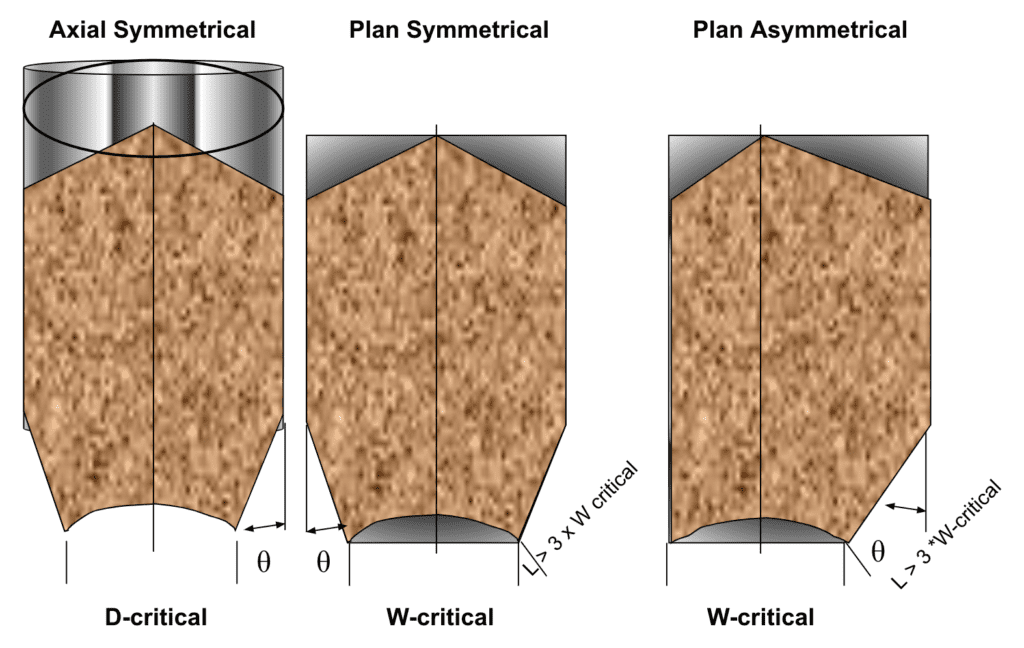
Critical Dimensions For Mass Flow Bins
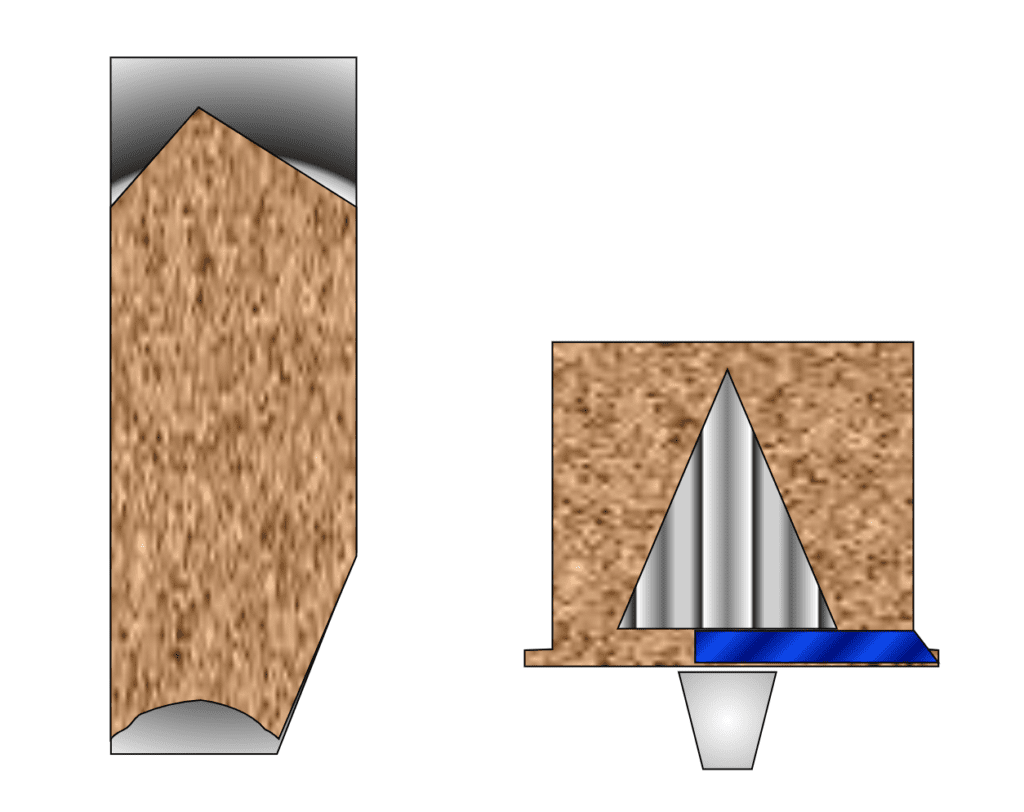
Plan Asymmetrical Design
Various Silo Designs
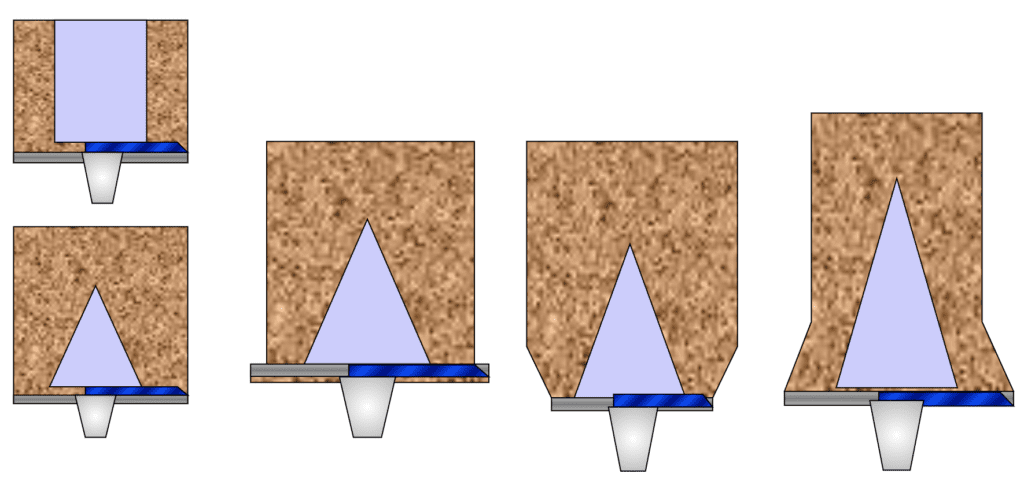
Theoretical Design
Bulk Materials that are very sensitive to compression and very sticky
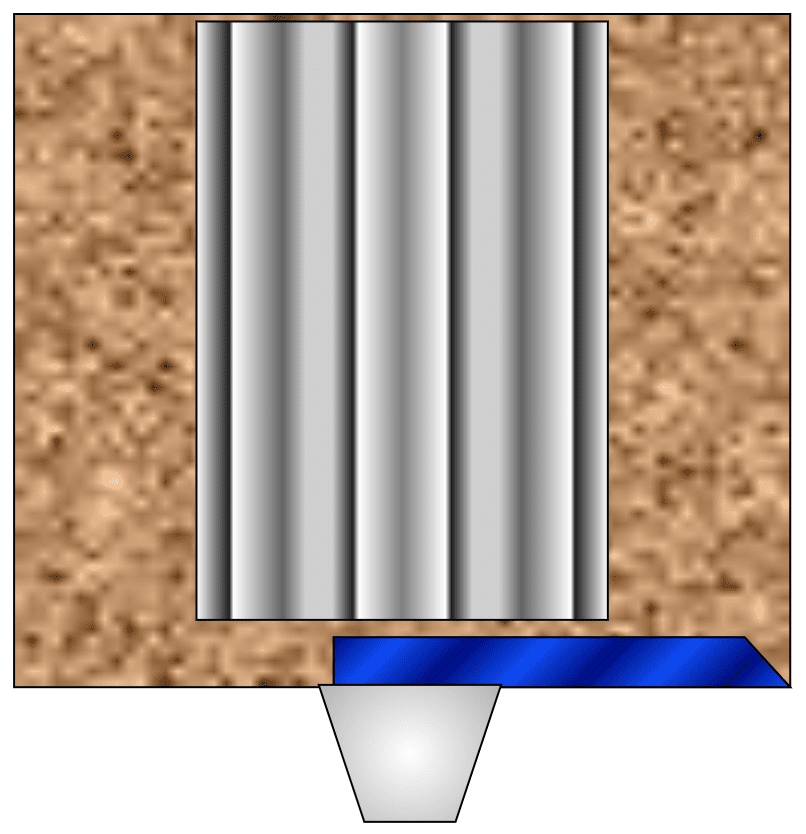
Design Without An “Undercut”
Bulk Material can build up in corners and compact at the floor
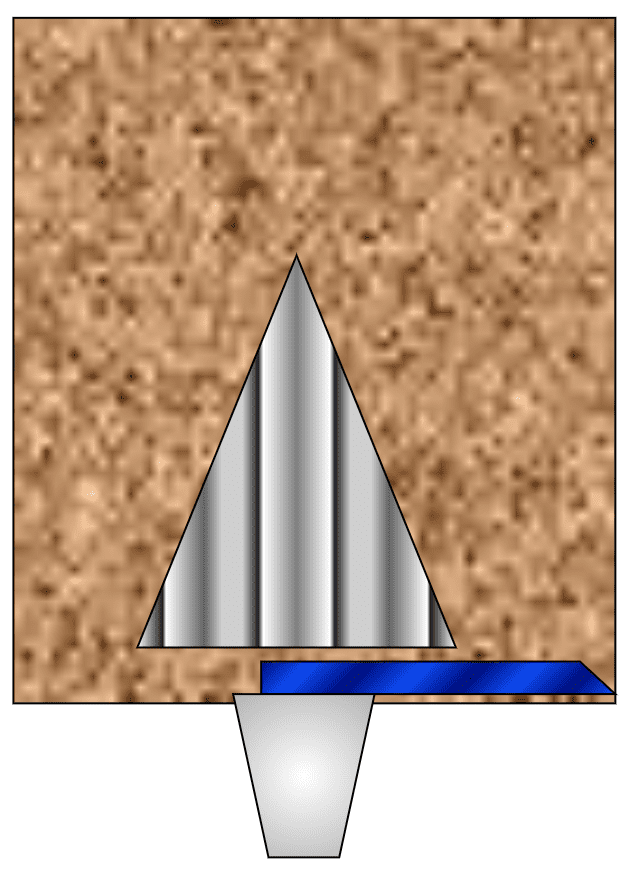
Easy Flow
Bulk Materials e.g. Mined Gypsum
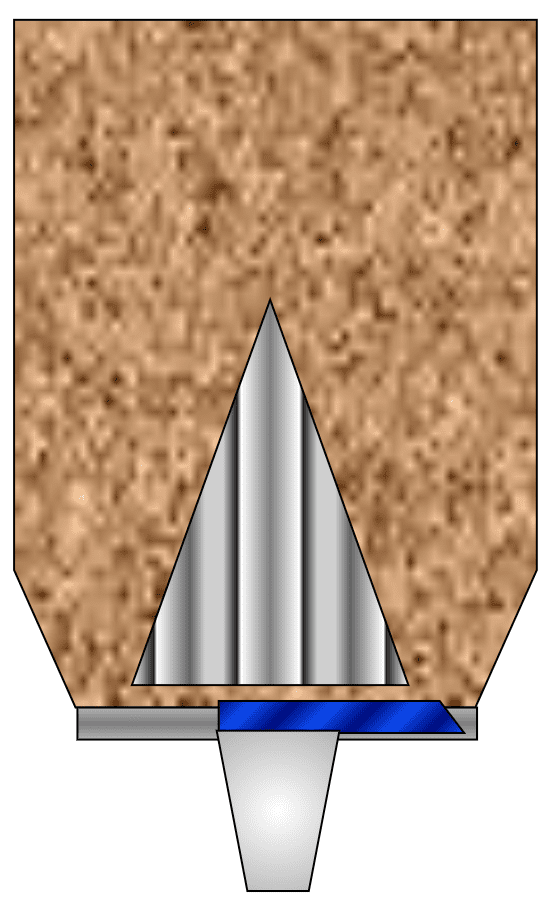
Sticky
Bulk Materials e.g. FGD Gypsum, Marl, Shale
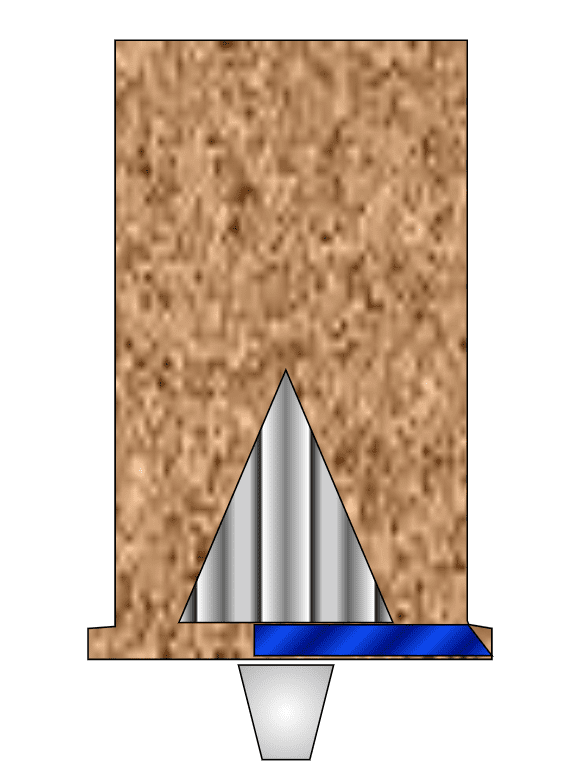
Very Sticky
Limits
- The analysis cannot be made with bulk materials having a high surface moisture like sewerage sludge.
- The particle size for the analysis has to be smaller than 1 mm.
- So the real situation inside a large silo cannot be really simulated, but the results are very conservative.


